This tutorial walks you through cracking WPA/WPA2 networks which use pre-shared keys. I recommend you do some background reading to better understand what WPA/WPA2 is. The Wiki links page has a WPA/WPA2 section. The best document describing WPA is Wi-Fi Security - WEP, WPA and WPA2. This is the link to download the PDF directly. The WPA Packet Capture Explained tutorial is a companion to this tutorial.
- Info@mysite.com +123-456-7890. (+) Awards & Fellowships (+) Education (+) Teaching (+) Publication (+) Download Vitae.
- WPA uses a 256 pre-shared key or passphrase for authentications. Short passphrases are vulnerable to dictionary attacks and other attacks that can be used to crack passwords. The following tools can be used to crack WPA keys. CowPatty– this tool is used to crack pre-shared keys (PSK) using brute force attack.
WPA/WPA2 supports many types of authentication beyond pre-shared keys. aircrack-ng can ONLY crack pre-shared keys. So make sure airodump-ng shows the network as having the authentication type of PSK, otherwise, don't bother trying to crack it.
Cracking: WEP and WPA PSK (WPA 1 and 2). It runs on: Linux (packaged for OpenWrt ), Windows, OS X, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris and even on eComStation 2. CPU architectures (x86 and 64 bit, ARM v7, ARM v8, PowerPC, etc).

There is another important difference between cracking WPA/WPA2 and WEP. This is the approach used to crack the WPA/WPA2 pre-shared key. Unlike WEP, where statistical methods can be used to speed up the cracking process, only plain brute force techniques can be used against WPA/WPA2. That is, because the key is not static, so collecting IVs like when cracking WEP encryption, does not speed up the attack. The only thing that does give the information to start an attack is the handshake between client and AP. Handshaking is done when the client connects to the network.Although not absolutely true, for the purposes of this tutorial, consider it true. Since the pre-shared key can be from 8 to 63 characters in length, it effectively becomes impossible to crack the pre-shared key.
The only time you can crack the pre-shared key is if it is a dictionary word or relatively short in length. Conversely, if you want to have an unbreakable wireless network at home, use WPA/WPA2 and a 63 character password composed of random characters including special symbols.
The impact of having to use a brute force approach is substantial. Because it is very compute intensive, a computer can only test 50 to 300 possible keys per second depending on the computer CPU. It can take hours, if not days, to crunch through a large dictionary. If you are thinking about generating your own password list to cover all the permutations and combinations of characters and special symbols, check out this brute force time calculator first. You will be very surprised at how much time is required.
IMPORTANT This means that the passphrase must be contained in the dictionary you are using to break WPA/WPA2. If it is not in the dictionary then aircrack-ng will be unable to determine the key.
There is no difference between cracking WPA or WPA2 networks. The authentication methodology is basically the same between them. So the techniques you use are identical.
It is recommended that you experiment with your home wireless access point to get familiar with these ideas and techniques. If you do not own a particular access point, please remember to get permission from the owner prior to playing with it.
Please send me any constructive feedback, positive or negative. Additional troubleshooting ideas and tips are especially welcome.
Wpa Psk Meaning
(Last Updated On: 06/08/2019)A WiFi-Penetest-Cracking tool for WPA/WPA2 (Handshake, PMKID, Offline Cracking, EAPOLS, Deauthentication Attack). WiFiBroot is built to provide clients all-in-one facility for cracking WiFi (WPA/WPA2) networks. It heavily depends on scapy, a well-featured packet manipulation library in Python. Almost every process within is dependent somehow on scapy layers and other functions except for operating the wireless interface on a different channel. That will be done via native linux command iwconfig for which you maybe need sudo privileges.

It currently provides four independent working modes to deal with the target networks. Two of them are online cracking methods while the other runs in offline mode. The offline mode is provided to crack saved hashes from the first two modes.
One is for deauthentication attack on wireless network and can also be used as a jamming handler. It can be run on a variety of linux platforms and at least requires WN727N from tp-link to properly operate.
Installation:
WiFiBroot heavily depends on scapy. So, you would need scapy installed. Almost, every other library would likely be installed on your system. Make sure the version you install for scapy should be <=2.4.0. Newer versions are likely to throw some unknown errors.
The script is supposed to be run under sudo but it will still work even if not run under the root mode. The basic necessary arguments are:
Documentation :
WiFiBroot uses modes to identify which attack you want to perform on your target. Currently, there are three available modes. The usage of each mode can be seen by supplying the –help/-h option right after the -m/–mode option. Here’s a list of available modes and what they do:
Modes:
Each mode has a specific purpose and has it’s own options:
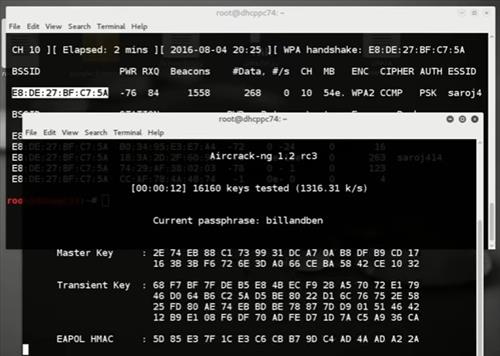
HANDSHAKE:
PMKID ATTACK:
Offline Cracking:
DEAUTHENTICATION ATTACK (Stress Testing)
Examples

To Capture 4-way handshake and crack MIC code:
To Capture and Crack PMKID:
Offline Crack Handshake and PMKID:
Wpa Psk Wpa2 Psk
Deauthentication attack in various form: